Advanced BCC Management
Systemic treatments for managing advanced or metastatic BCC (mBCC) that cannot be treated with conventional methods, including Hedgehog pathway inhibitors and immunotherapy, are the cornerstones of treatment for these cases.1
In specific populations, such as the immune-suppressed, the elderly, those with poor baseline functional status, and cases of metastatic, advanced, recalcitrant, or cosmetically sensitive disease, nonsurgical management may be a desirable alternative.2 BCC rarely reaches an advanced stage, so systemic chemotherapy is not typically used to treat these cancers.3
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors
Aberrant signaling in the Hedgehog pathway is a principal driver in BCC’s progression and pathogenesis.4
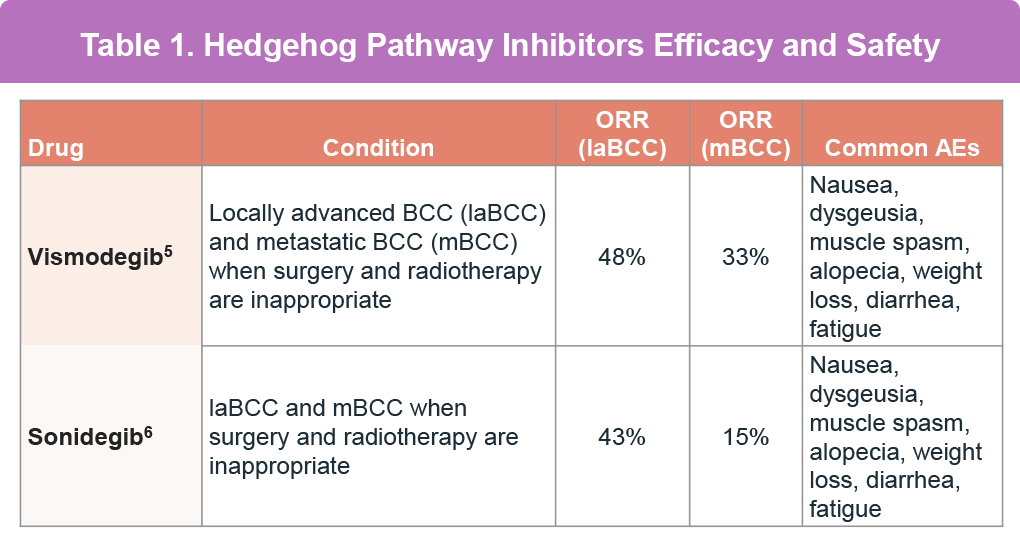
Vismodegib and sonidegib, hedgehog pathway inhibitors, have been FDA-approved for treatment (Table 1).
The effectiveness of these treatments is limited by the development of resistance, which reduces their efficacy.1 Additionally, these therapies often lead to serious adverse events, such as ageusia/dysgeusia, muscle spasms, alopecia, and weight loss, causing discontinuation.7 Therefore, according to the NCCN guidelines, drug holidays or alternative dosing schedules are recommended to manage side effects, improve adherence to therapy, and enhance the quality of life for patients. For patients who no longer benefit from or cannot tolerate hedgehog pathway inhibitors, immunotherapy with cemiplimab is recommended.1
Immunotherapy
Cemiplimab and pembrolizumab are immunotherapy drugs that target the PD-1 receptor on T-cells. Normally, PD-L1 proteins on peripheral tissues and tumor cells bind to PD-1 receptors, sending inhibitory signals that suppress T-cell activity and proliferation. By blocking this interaction, these drugs enhance the anti-tumor immune response of T cells, countering the immune-suppressive environment created by tumors.4
One small study also aimed to explore the combined effect of Hedgehog pathway inhibitors and immunotherapy, investigating pembrolizumab and vismodegib. Additionally, cemiplimab, pembrolizumab, and nivolumab with or without relatlimab are being investigated in the neoadjuvant setting. Pembrolizumab is being investigated in the adjuvant setting. Refer to the Immunotherapy in cSCC tab to review the study details.
Systemic treatments, such as Hedgehog pathway inhibitors and immunotherapy show promise in managing advanced and metastatic BCC. While Hedgehog pathway inhibitors have proven effective, dealing with resistance and adverse effects remains challenging. It is crucial to follow treatment guidelines because there is still much to learn about the best use of existing systemic inhibitors of the hedgehog pathway and the discovery of new therapies that can achieve high response rates with fewer side effects. Determining the best treatment approach often requires input from multiple specialists, considering the individual patient’s condition and response to treatment.9
References
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Basal Cell Skin Cancer. Version 1.2026. Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nmsc.pdf
- Lanoue J, Goldenberg G. Basal cell carcinoma: A comprehensive review of existing and emerging nonsurgical therapies. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2016;9:26-36. PMCID: PMC4928477
- American Cancer Society. Systemic chemotherapy for basal and squamous cell skin cancers. Last revised October 31, 2023. (https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/basal-and-squamous-cell-skin-cancer/treating/systemic-chemotherapy.html).
- Bakshi A, Chaudhary SC, Rana M, Elmets CA, Athar M. Basal cell carcinoma pathogenesis and therapy involving hedgehog signaling and beyond. Mol Carcinog. 2017;56:2543-2557. doi:10.1002/mc.22690
- Sekulic A, Migden MR, Lewis K, et al. Pivotal ERIVANCE basal cell carcinoma (BCC) study: 12-month update of efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced BCC. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:1021-1026.e8. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.03.021
- Migden MR, Guminski A, Gutzmer R, et al. Treatment with two different doses of sonidegib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma (BOLT): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:716-728. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70100-2
- Sekulic A, Yoo S, Kudchadkar R, et al. Real-world assessment and treatment of locally advanced basal cell carcinoma: Findings from the RegiSONIC disease registry. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0262151. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0262151
- Stratigos AJ, Sekulic A, Peris K, et al. Cemiplimab in locally advanced basal cell carcinoma after hedgehog inhibitor therapy: an open-label, multi-centre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:848-857. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00126-1
- Work Group; Invited Reviewers, Kim JYS, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:540-559. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.10.006
- Lewis KD, Peris K, Sekulic A, et al. Final analysis of phase II results with cemiplimab in metastatic basal cell carcinoma after hedgehog pathway inhibitors. Ann Oncol. 2024;35:221-228. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2023.10.123
All URLs accessed September 12, 2025